Understanding Load Cell Technology
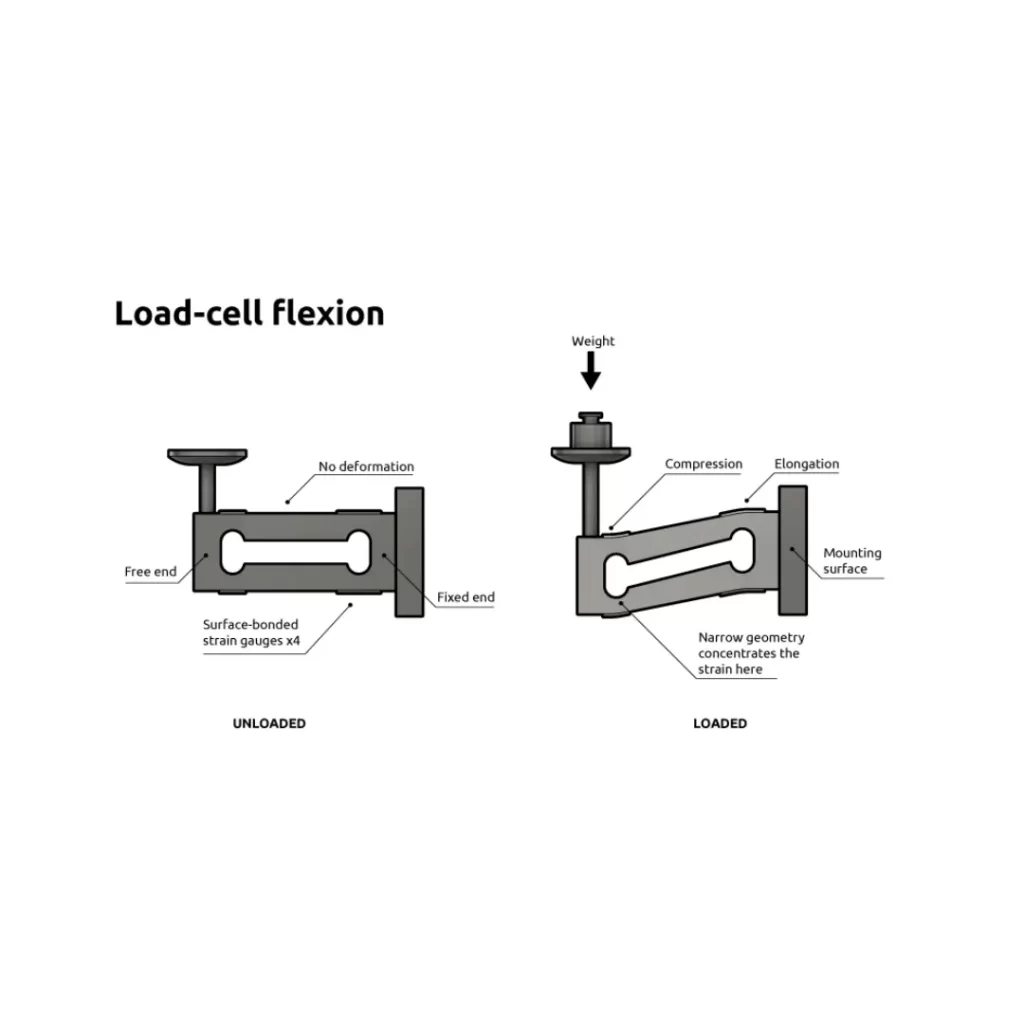
A load cell is a transducer that converts mechanical force into a measurable electrical output. The core principle behind this technology is based on the deformation of a strain gauge, a device that undergoes physical change when pressure is applied, thus altering its electrical resistance. This change in resistance is then measured, calibrated, and converted into units of force or weight.
Applications & Advantages of Handheld Element Analyzers

Handheld element analyzers have become indispensable in various industries for their ability to quickly and accurately determine the elemental composition of materials. These portable devices ensure that stringent quality control measures are met, environmental regulations are adhered to, and manufacturing processes are optimized for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The Explorer 5000, a standout among these devices, exemplifies the advancements in handheld XRF technology. Here’s a closer look at the wide-ranging applications of these analyzers and the distinctive advantages of the Explorer 5000.
Factors to Consider before Buying a Gold Testing Machine

When it comes to the precious metals business, accuracy is the bedrock upon which trust and customer satisfaction are built. A gold testing machine is an indispensable tool for jewelers, pawnbrokers, and precious metal dealers. The right machine can mean the difference between a reputation for reliability and the costly mistakes of inaccuracy. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you make an informed decision when purchasing a gold testing machine for your business.
Traditional Gold Melting Vs Metro Gold Melting Machines

Induction heating is recognized as an environmentally friendly technology because it produces no harmful emissions, thanks to the generation of heat through an alternating magnetic current directed into a graphite crucible. Additionally, this method offers several benefits for gold casting, such as rapid heating times and frequency stirring, which results in more uniform melts. Moreover, induction melting technology maintains a cooler surrounding environment for the operator, as the only heat produced is directly from the melting process itself.
What is XRF Technology
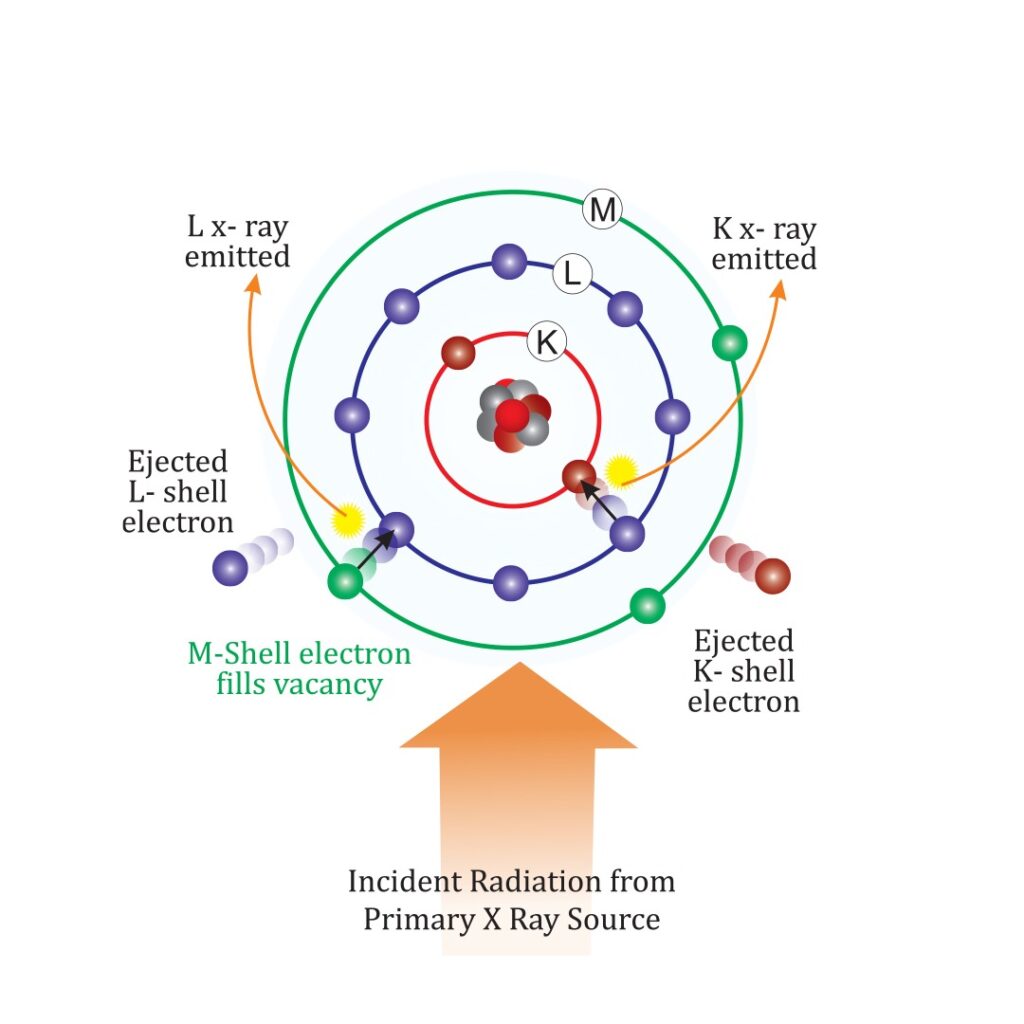
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is an analytical technique which uses the interaction of x-rays with a target material to determine its elemental composition. XRF is a totally safe, non-destructive method. The technology of the analyser is based on energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence using an X-ray tube as the source of excitation. The range of detectable elements varies according to the individual instrument’s configuration, but typically EDXRF covers all elements from sodium (Na) to uranium (U). Concentrations can range from ‘100%’ down to ‘ppm’ (and in some cases sub-ppm) levels. XRF is a “non-destructive” process, which means there is no need to physically scrape, remove or damage the sample item to determine the outcome. XRF spectrum analysers are widely used in Industries as diverse as precious metals, alloys, toys, electrical/ electronic, environmental and mining.
X-ray fluorescence involves the emission of characteristic fluorescent Xrays from a material which has been excited by bombarding it with highenergy X-rays or gamma rays. X-ray fluorescence can be considered as a simple, three-step process occurring at the atomic level. First, an incoming X-ray knocks out an electron from one of the orbital’s surrounding the nucleus within an atom of the material. A ‘hole’ is produced in the orbital, resulting in a high- energy unstable configuration for the atom. To restore equilibrium, an electron from a higher-energy, outer orbital falls into the hole. Since this is a lowerenergy position, the excess energy is emitted in the form of a fluorescent X-ray. This is the ‘Energy Dispersive’ aspect of the process and it is this energy which is measured by the equipment.
The difference in energy between the expelled and the replacement electrons is characteristic of the element atom in which the fluorescence process is occurring – thus, the energy of the emitted fluorescent X-ray is directly related to the specific element being analysed. It is this key feature which makes XRF such a fast analytical tool for elemental composition.
